North Edge C-NEXUS The Lightweight Outdoor Watch

Hey everyone!
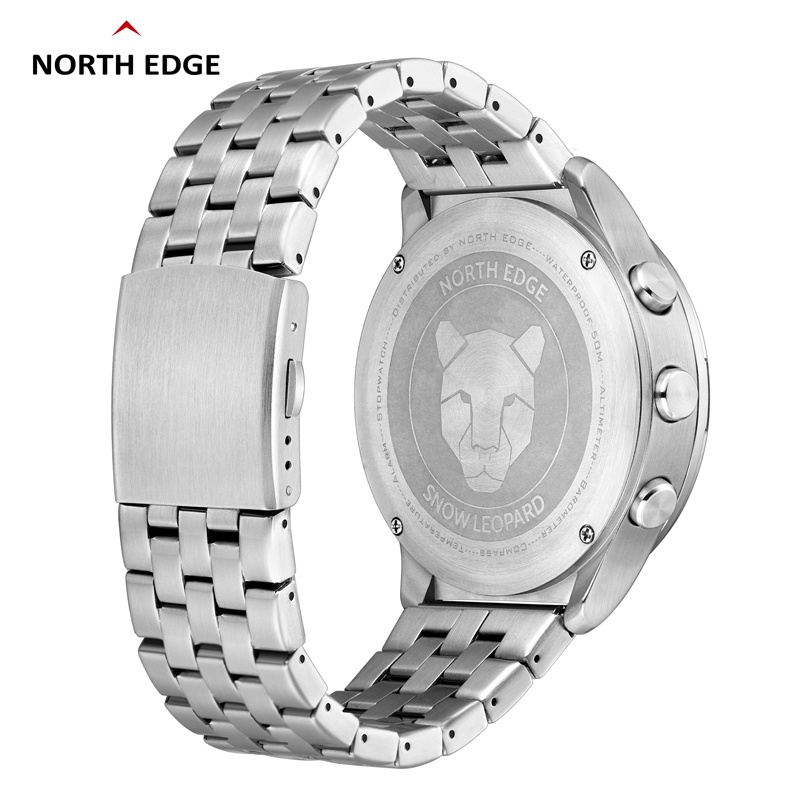
Father's Day is coming up, and I want to share an amazing gift option - the Snow Leopard watch.
This watch is truly extraordinary. It not only tells time accurately with its hour, minute, second, year, month, and day display, but also has a 12/24H system. It offers a whole range of practical functions like atmospheric pressure measurement, altitude measurement, stopwatch, compass, alarm, thermometer, and a second time function. The backlight is handy, and the sleep function is a nice touch.
It's a combination of style and functionality that any father would love to have on his wrist. It's the ideal way to show our appreciation and love for our dads this Father's Day.
Don't miss out on this great gift choice!



First, let's discuss the causes of low-frequency vibrations.
Repeated tests have shown that low-frequency vibrations are primarily caused by the resonances of the building. The construction specifications for industrial and civil buildings are generally similar in terms of floor height, depth, span, beam and column sections, walls, floor beams, raft slabs, etc. Although there may be some differences, particularly regarding low-frequency resonances, common characteristics can be identified.
Here are some patterns observed in building vibrations:
1. Buildings with linear or point-shaped floor plans tend to exhibit larger low-frequency resonances, while those with other shapes such as T, H, L, S, or U have smaller resonances.
2. In buildings with linear floor plans, vibrations along the long axis are often more pronounced than those along the short axis.
3. In the same building, the first floor without a basement typically experiences the smallest vibrations. As the floor height increases, the vibrations worsen. The vibrations in the first floor of a building with a basement are similar to those in the second floor, and the lowest vibrations are typically observed in the lowest level of the basement.
4. Vertical vibrations are generally larger than horizontal vibrations and are independent of the floor level.
5. Thicker floor slabs result in smaller differences between vertical and horizontal vibrations. In the majority of cases, vertical vibrations are larger than horizontal vibrations.
6. Unless there is a significant vibration source, vibrations within the same floor of a building are generally consistent. This applies to locations in the middle of a room as well as those near walls, columns, or overhead beams. However, even if measurements are taken at the same location without any movement and with a few minutes interval, the values are likely to differ.
Now that we know the sources and characteristics of low-frequency vibrations, we can take targeted improvement measures and make advanced assessments of the vibration conditions in certain environments.
Improving low-frequency vibrations can be costly, and sometimes it is not feasible due to environmental constraints. Thus, in practical applications, it is often advantageous to choose or relocate to a better site for operating an electron microscope laboratory.
Next, let's discuss the impact of low-frequency vibrations and potential solutions.
Vibrations below 20 Hz have a significant disruptive effect on electron microscopes, as depicted in the following figures.
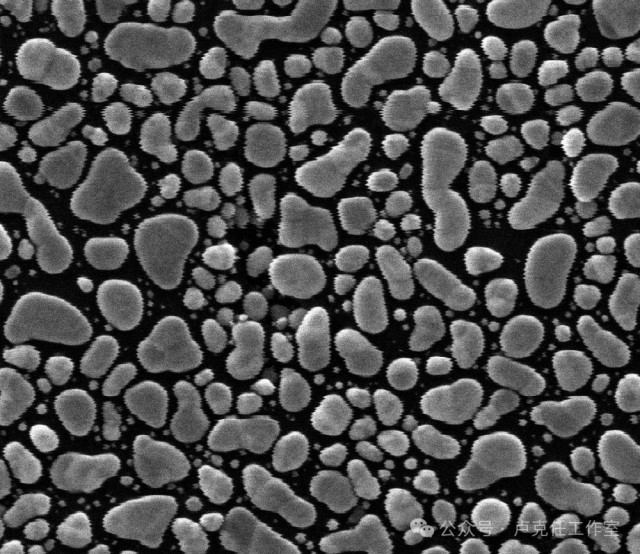
Image 1
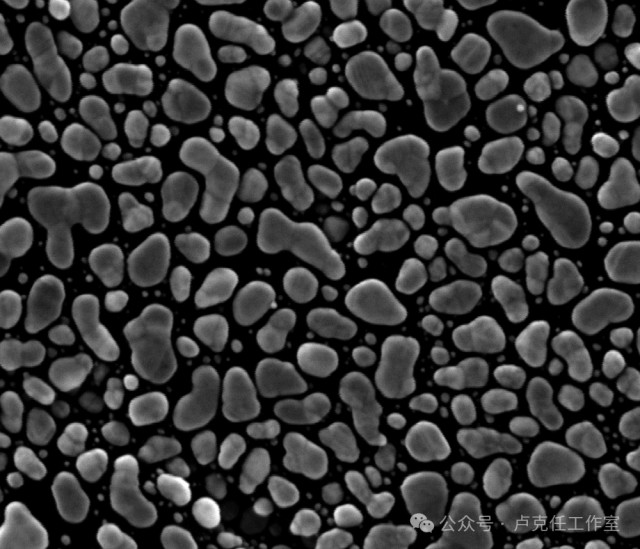
Image 2
Image 1 and Image 2 were taken by the same Scanning Electron Microscope (both at 300kx magnification). However, due to the presence of vibration interference, Image 1 has noticeable jaggedness in the horizontal direction (in segments), and the clarity and resolution of the image are significantly reduced. Image 2 is the result obtained from the same sample after eliminating the vibration interference.
If the test results indicate that the location where the microscope is to be installed has excessive vibrations, appropriate measures must be taken; otherwise, the microscope manufacturer cannot guarantee that the performance of the microscope after installation can meet the optimal design standards. Generally, several methods can be chosen to improve or solve the issue, such as using an Anti-Vibration Foundation, Passive-Vibration Isolation Platform, or Active-Vibration Isolation Platform.
An Anti-Vibration Foundation requires on-site construction and special measures need to be taken (such as having an elastic cushion layer at the bottom and surrounding areas). Conventional construction methods may potentially increase low-frequency vibrations (below 20Hz). The construction process involving a large amount of construction materials coming in and out may inevitably affect the surrounding environment. A schematic diagram of an Anti-Vibration Foundation can be seen in Image3.
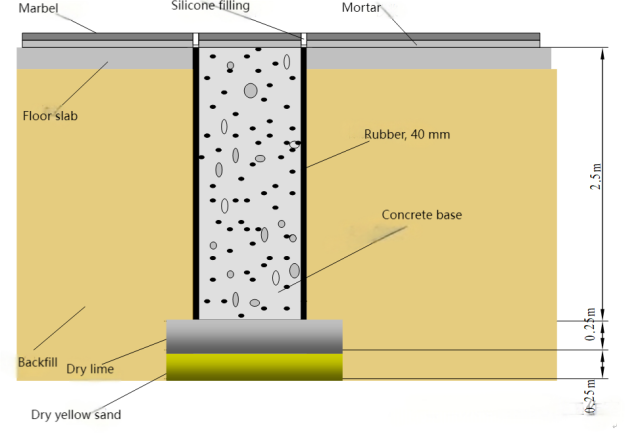
Image3
A concrete vibration isolation platform with a mass of around 50 tons generally achieves a vibration reduction effect of -2 to -10dB at frequencies above 2Hz. The larger the mass of the concrete vibration isolation platform, the better the vibration reduction. If conditions permit, it should be made as large as possible.
Based on multiple tests conducted in different locations, vibration isolation platforms weighing less than 5 tons exhibit resonance in the low-frequency range of 1-10Hz, which increases vibration. Those weighing less than 20 tons are ineffective, and the effective range starts at over 30 tons. No data is available for 30-40 tons, so it is advisable to avoid weights below 50 tons. A university in Beijing has achieved good results with a vibration isolation platform weighing around 100-200 tons. In a research institute in Chongqing, the ground concrete was directly poured on massive rocks, resulting in minimal vibration.
Among passive vibration dampers, commonly used options like rubber, steel springs, and air springs (cylinders) provide poor performance in the low-frequency range below 20Hz. They often amplify vibrations due to resonance, so they are not considered suitable.
Only magnetic dampers show acceptable low-frequency performance, but their performance is still far inferior to active dampers (similar to the vibration reduction effect of concrete vibration isolation platforms). Figure 4 compares the effectiveness of several methods.
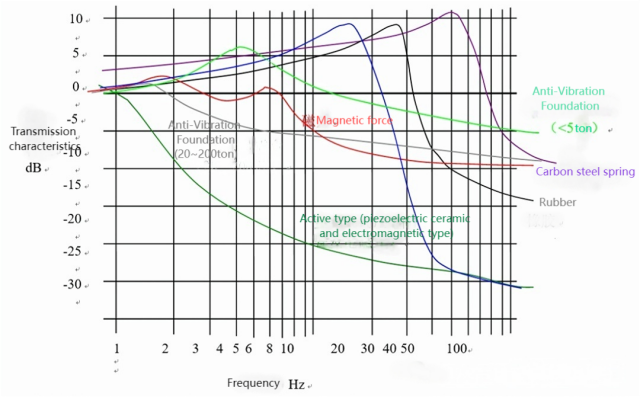
Figure 4
Upon careful observation of Figure 4, we can draw the following conclusions:
1. The resonance frequency (fh) of the carbon steel spring is approximately 50 Hz. It does not provide any damping effect below 70 Hz and, in fact, amplifies the vibration due to resonance. The rubber pad has an fh of approximately 25 Hz and does not provide any damping effect below 35 Hz, also amplifying the vibration due to resonance.
2. Concrete dampers with a capacity below 5 tons exhibit resonance below 10 Hz and are often less effective than not using a damper at all.
3. Air springs have an fh of approximately 15 Hz, providing good damping above 25 Hz and excellent damping above 40 Hz. They are widely used for vibration isolation in precision equipment such as optical platforms. However, they exhibit significant resonance below 20 Hz, making them unsuitable for damping electron microscopes (although some electron microscopes do use air springs as a last resort).
4. Magnetic dampers provide satisfactory low-frequency damping and can be used when strict requirements are not imposed.
5. Various active dampers achieve excellent damping effects. Their resonance frequencies can be below 1 Hz, and they can provide damping up to -10 to -22 dB in the 2-10 Hz range, making them ideal for applications requiring effective damping in the low-frequency range.
In general, vibrations below 20 Hz are considered to have a significant impact on electron microscopes and are difficult to mitigate. Since most people cannot perceive vibrations below 20 Hz, it often leads to a misconception that there is no vibration when significant low-frequency vibrations are present.
Passive dampers utilize the physical properties of damping devices, such as their mass and inherent vibration transmission characteristics, to isolate and attenuate external vibrations affecting the electron microscope. The working principle of passive dampers can be referenced in Figure 5.
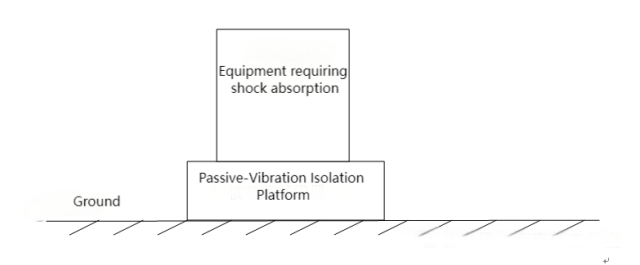
Figure 5
The working principle of active dampers is significantly different from passive dampers. Various types of active dampers have similar working principles, which involve a three-dimensional sensor detecting external vibrations in three directions. The sensor sends the information to a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller, which generates control signals with equal amplitude but opposite phase. These control signals are then used by an actuator to generate internal vibrations with equal amplitude and opposite phases to counteract or reduce the external vibrations. The working principle of active dampers can be referred to as shown in Figure 6.
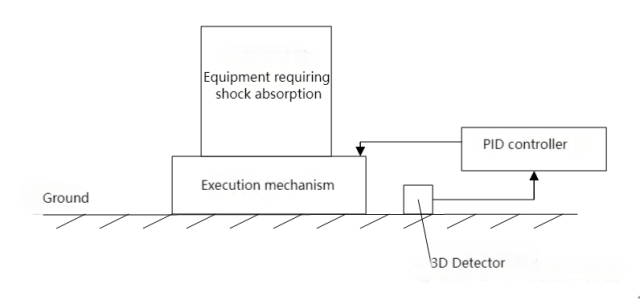
Figure 6
Active dampers commonly used include piezoelectric ceramic dampers, pneumatic dampers, and electromagnetic dampers. Their differences mainly lie in the actuation mechanism, while 3D detectors and PID controllers are relatively similar.
Piezoelectric Ceramic Dampers:
They utilize the piezoelectric effect of the ceramic material to generate three-dimensional internal vibrations with equal amplitude and opposite phase.
Pneumatic Dampers:
Controlled by a PID controller, the inlet and outlet valves modulate the continuous compressed air in a special cylinder to generate three-dimensional internal vibrations with equal amplitude and opposite phase.
Electromagnetic Dampers:
The PID controller controls three sets of electromagnetic coils to generate three-dimensional internal vibrations with equal amplitude and opposite phase.
Active dampers can achieve vibration reduction effects of approximately -22 to -28 dB above 20 Hz (although there have been claims of achieving -38 dB, they are mostly unsubstantiated).
Different types of active dampers also have significant price differences. Generally, the dampers are prepared before the electron microscope is installed and are installed simultaneously with the microscope.
In addition, under specific conditions, a vibration isolation trench can also achieve good damping effects.
Figure 7 depicts a situation where the vibration isolation trench is.
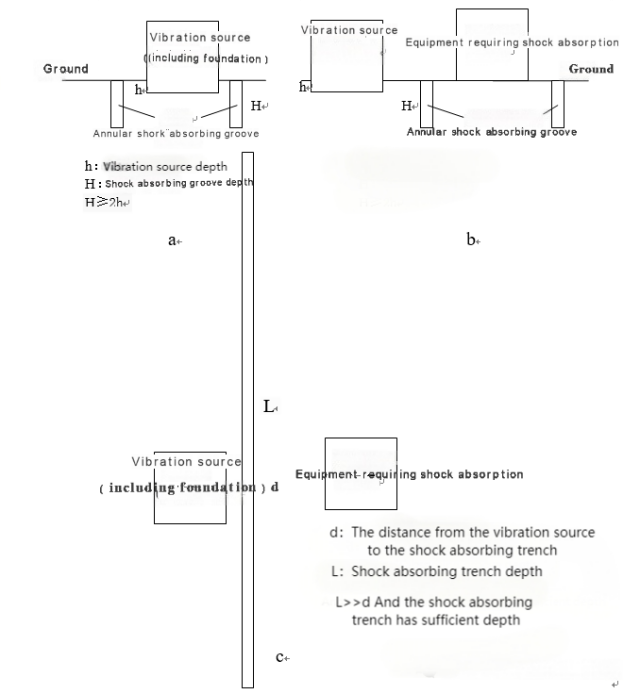
Figure 7
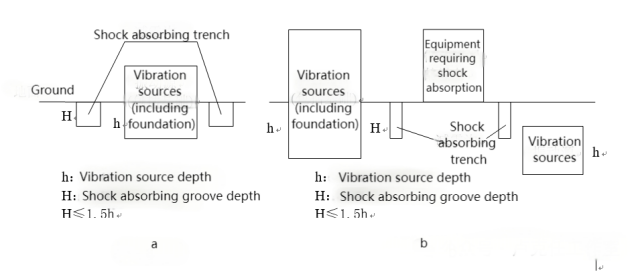
Figure 8
Figure 8 represents an ineffective scenario for a vibration trench.
In general, the deeper the vibration trench, the better the damping effect (the width of the trench has little impact on the damping effect). Here is a comparison of several common damping methods:
|
Type
|
Carbon Steel Spring |
Rubber Dampers
|
Anti-Vibration Foundation |
Magnetic Dampers |
Air Spring (Cylinder) |
Active Dampers |
|
|
Price |
Lowest |
Low |
Medium |
Low |
High |
Highest |
|
|
Damping Performance |
1~5Hz |
Poor |
Poor |
Medium |
Poor |
Poor |
Excellent |
|
5~20Hz |
Poor |
Poor |
Medium |
Medium |
Poor |
Excellent |
|
|
20~50Hz |
Poor |
Medium |
Medium |
Good |
Medium |
Excellent |
|
|
>50Hz |
Good |
Good |
Medium |
Good |
Good |
Good |
|
|
Installation and Adjustment Difficulty |
Easy |
Easy |
Difficult |
Easy |
Medium |
Difficult |
|
|
Energy Consumption |
None |
None |
None |
None |
A small amount of compressed gas |
>300w |
|
|
Routine Maintenance |
None |
None |
None |
None |
Required |
Required |
|
|
Appearance |
Integrated/ Separate |
Integrated/ Separate |
Concealed underground |
Separate |
Separate + Flat panel |
Integrated/ Separate+ Flat panel
|
|
Introduction:
In today's fast-paced technological landscape, accurate measurements play a pivotal role in various industries. Among these measurements, determining DC current holds immense significance, and one reliable method is through the utilization of the Hall effect sensor. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the intricacies of measuring DC current using Hall effect sensors and unveil the fascinating principles behind this advanced technology.
1. Understanding the Hall Effect Phenomenon:
The Hall effect, named after its discoverer Edwin Hall, describes the generation of a voltage across a conductor when an electric current and a magnetic field are applied perpendicular to each other. This phenomenon forms the foundation of Hall effect sensors, which exploit this voltage generation for precise current measurements.
2. Components Required for DC Current Measurement:
To measure DC current using a Hall effect sensor, certain components must be gathered. These include the DC Current sensor itself, a power source, a magnet, and appropriate connection cables. Additionally, an instrumentation amplifier and an analog-to-digital converter may be employed for enhanced accuracy and digital signal processing.
3. Hall Effect Sensor Installation and Calibration:
The installation process involves placing the Hall effect sensor in proximity to the conductor carrying the DC current. Proper positioning and alignment of the sensor are essential for accurate measurements. Calibration ensures that the sensor's output corresponds precisely to the current being measured, eliminating any potential inaccuracies.
4. Signal Conditioning and Voltage Measurements:
The voltage generated by the Hall effect sensor is typically very small and requires amplification for reliable measurements. Signal conditioning techniques, such as filtering and amplification, are employed to enhance the sensor's output signal. Once conditioned, the voltage is converted to a measurable quantity using an analog-to-digital converter.
5. Data Analysis and Interpretation:
With the obtained voltage readings, precise calculations can be performed to determine the DC current passing through the conductor. Calibration factors and sensor specifications play a vital role in ensuring accurate and precise measurements. Proper data analysis techniques facilitate the extraction of meaningful insights from the measured current values.
Conclusion:
Measuring DC current using Hall effect sensors provides a reliable and non-intrusive method for various applications, ranging from power electronics to automotive systems. The principles behind the Hall effect phenomenon, combined with careful installation, calibration, and signal conditioning, enable accurate and robust current measurements. By harnessing the power of Hall effect sensors, engineers and researchers can pave the way for innovative advancements and ensure the efficient utilization of electrical energy in diverse industries.
Hall current sensors are an invaluable component in various industries, providing precise and reliable measurement of electrical currents. However, they face a constant challenge – interference. To ensure accurate readings, these sensors must possess exceptional anti-interference capabilities that shield them from external influences.
The need for anti-interference capability in Hall current sensors arises from the complex electrical environments they operate in. With the proliferation of electronic devices, electromagnetic fields pervade our surroundings, emanating from power lines, motors, and other sources. These electromagnetic interferences can distort the sensor's output, leading to inaccuracies and compromising their functionality.
To tackle this issue, Hall current sensors are meticulously designed to combat interference. Their construction involves robust shielding materials that effectively deflect external electromagnetic fields. Additionally, advanced electronic filtering techniques are employed to suppress noise and extraneous signals, ensuring the sensor focuses solely on the desired current measurements.
Anti-interference capability is especially crucial in applications where accuracy is paramount. In industrial settings, for instance, where machinery operates in close proximity to sensitive electronic equipment, even the slightest interference can result in significant errors. Thus, these sensors must possess a high level of immunity to electromagnetic disturbances.
Moreover, anti-interference capability is vital when monitoring electrical currents in complex systems. For instance, in smart grid networks, where multiple sources and loads coexist, the sensor must discern the desired current from an array of overlapping waveforms. By effectively rejecting unwanted signals, these sensors ensure accurate and reliable measurements, enabling efficient energy management.
Furthermore, anti-interference capability is essential in safety-critical applications. For instance, in the automotive industry, where Hall current sensors are utilized in electric vehicle charging systems, any interference could jeopardize the charging process and compromise user safety. Hence, these sensors must offer superior anti-interference performance to ensure seamless and secure operation.
In conclusion, the significance of anti-interference capability in Hall current sensors cannot be overstated. By shielding against external electromagnetic fields and employing advanced filtering techniques, these sensors provide accurate and reliable measurements in complex electrical environments. Their ability to resist interference is crucial for applications requiring precision and safety, making them in numerous industries. Njtokensensor is a professional Hall effect sensor manufacturer, get more details from us quickly.

Currently, outdoor advertising signs have become an integral part of the city. These advertising signs make cities more lively and vibrant by attracting people's eyes. Among them, LCD advertising signs are one of the most popular types of outdoor advertising.
LCD advertising signs have many advantages. First of all, the display effect of this kind of advertising signs is very good. It uses an LCD screen to display advertising information, and this screen can produce a very clear and bright picture that is also clearly visible in the sunlight. This means that the LCD signage can show excellent visual effects during the day and night, even under adverse weather conditions.
Secondly, LCD signage allows advertisers to change the content of their ads at any time. For traditional signs, if an advertiser wants to change the content of the advertisement, he needs a special worker to replace the sign. However, LCD signage can change the content of the advertisement at any time by electronic means without changing the sign.
In addition, LCD advertising signs also have good durability. These advertising signs are usually made of high quality materials and are waterproof, windproof, and UV-proof. This allows them to work for long periods of time in outdoor environments and not be damaged.
All in all, LCD advertising signage is a very practical type of outdoor advertising. It allows advertisers to get better publicity effect through its comfortable visual effect, flexibility to change the advertisement content at any time and excellent durability, and also creates a more vivid and lively atmosphere for the city.

1. Good display effect: Outdoor LCD digital advertising signage has very good display effect, bright colors, not easily affected by sunlight and rain, and can maintain a clear picture display in various environments.
2. High reliability: Outdoor LCD digital signage has high reliability and can adapt to the harsh environmental requirements such as wide temperature range, high humidity and atmospheric pressure changes to ensure long and stable operation.
3. Cost saving: Outdoor LCD digital signage does not require complex installation, maintenance and operation costs, and can be controlled remotely to improve operational efficiency and reduce operating costs.
4. Customizable: Outdoor LCD digital signage can be customized according to customer needs, including size, resolution, brightness, installation methods, etc., to adapt to different scenarios and needs.
5. Safe and reliable: Outdoor LCD digital advertising signage is designed with waterproof, dustproof and lightning-proof, which can ensure the safety and reliability of the equipment and avoid damage caused by natural disasters or other external factors.

Window Facing High Brightness LCD Display widely used in indoor situations,such as restaurants,shops,super markets,airport and subway stations. Normally the indoor advertising display uses LCD product from 32 inch to 86 inch. Floor standing and wall mounted are both available. We can add a touch panel if you need the interact function, such as search the locations and destinations in the shopping mall. It makes people’s life more interesting and intelligent.
Now most of the digital signage’s brightness is about 350-500 nits,it’s difficult to meet the commercial needs . Simultaneously the buildings use high brightness lighting sources ,shopping malls and airport terminals use transparent roofs, those make the low brightness digital advertising display looks very badly.

If the lcd digital advertising display looks badly when facing to strong lighting sources,then it’s time to upgrade the digital signage to a high brightness indoor advertising display , which supports 1500 cd/m2 or more. Its screen is bright enough to show the advertised product clearly.It’s very helpful to promote products.
The high brightness lcd digital signage is more and more widely used everywhere,specially in restaurants and shop windows. Most of the shop windows are facing to outside,where is very bright. So it’s necessary to install an high brightness window advertising display, it helps you to show the products to the people who go pass your window.


Now the brightness of digital window display is up to 4000cd/m2,the high brightness digital display helps you to solve the reflection problem because of the dark advertising display.
The high brightness digital signage normally use the industrial grade panel from LG or BOE. And it supports auto dimming function, which works according to the ambient light. That helps to cut down the power consumption.
What’ more,we’re very experienced to adjust the contrast ratio and color gamut, that’s very important for a high definition LCD screen.
The high bright digital signage supports to be spliced,within 5mm gaps, which is suitable for a large area window advertising display. get more products details at www.cnlcdisplay.com.

With the development of economy and the progress of technology, LCD outdoor digital signage has gradually become an important and indispensable equipment in urban construction. With the advantages of high definition, wide angle view and good brightness, LCD outdoor digital signage is widely used in public transportation, advertising and weather forecasting, providing important information services for urban life and operation.
First of all, outdoor LCD digital signage has the characteristics of high definition. It adopts imported raw materials and high-end equipment, and carries out a variety of high-precision processing in the production process, which can present clearer and more delicate images, not only presenting good effects, but also long life span, and can withstand harsh climatic and environmental conditions.

In addition, the LCD outdoor digital signage has the feature of wide angle view. This digital signage adopts the latest LCD panels with a wider field of view, allowing more angles to be used to view information. In the process of outdoor information distribution, the wider the field of view area, the more it can attract people's attention. By using LCD outdoor digital signage, information will be conveyed more quickly and accurately.
Another advantage of LCD outdoor digital signage is its high brightness. It uses LED backlight technology, and its brightness is higher than that of ordinary LCD LCD screens. By adjusting the brightness under stronger sunlight, the outdoor digital signage can maintain a brighter display, thus enabling people to understand and get the message more clearly without the interference of sunlight.
In a word, LCD outdoor digital signage is a kind of digital display device with high definition and high brightness and wide angle view, which is suitable for advertising, weather forecast, public transportation and other fields. As urbanization accelerates and the demand for information services continues to escalate, LCD outdoor digital signage will certainly play an increasingly important role and bring higher quality displays and services.
In fast-paced days, outdoor advertisement has become an important way for companies to attract attention. However, traditional outdoor LCD advertising display often appear dim due to the impact of sunlight and cannot effectively convey information. But now, we are proud to launch a aluminum outdoor high-brightness LCD display, with its extremely high brightness and visibility under sunlight, let your brand shines outdoors.

The high brightness outdoor LCD display from CNLC adopts advanced high brightness backlight technology, ensuring that it can keep a bright and clear images(or videos) under strong sunlight. At the same time, our product is equipped with an ultra efficient heat dissipation system and pre heating system. No matter in summer or winter, our LCD display can work stably and without impact by temperature fluctuations. Whether the shops are along the street, in waiting area at a station or a stadium,our outdoor LCD display effortlessly catch the eye of the audience.

In order to solve the problem of reflection and interference in outdoor environment, the high brightness outdoor LCD display is equipped with professional anti-reflection coating and anti light interference technology. These technologies can effectively reduce the reflection of sunlight, provide better visibility for the LCD screen, ensure that the media contents are clearly visible, and facing direct sunlight, the customers can easily capture all details of advertised product.