Optimizing Warehouse Efficiency A Dive into RFID Technology

The Role of RFID Readers and Tags in Warehouse Goods Localization
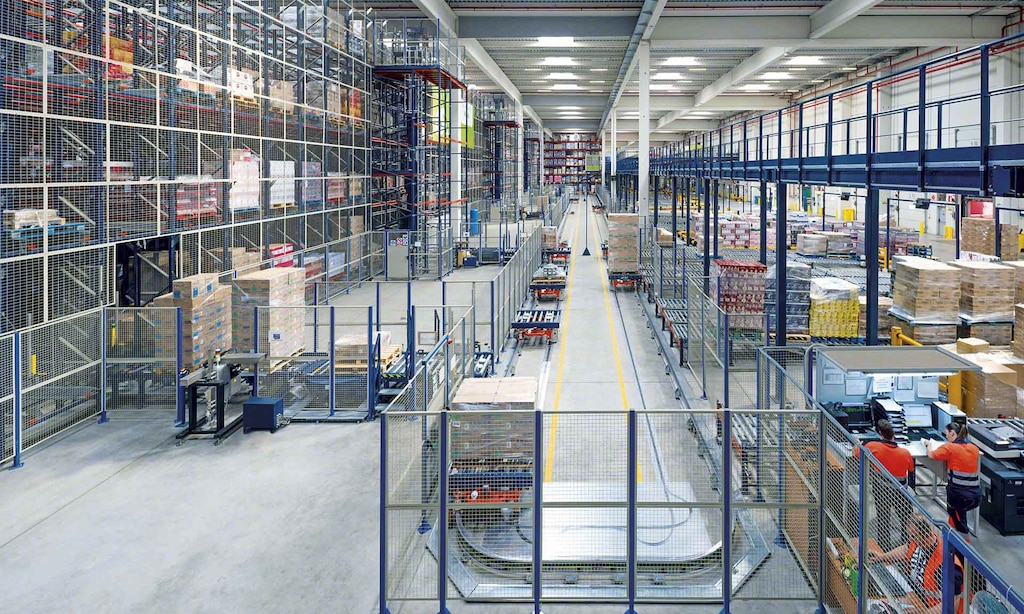
As the logistics and warehousing industries rapidly develop, efficiently and accurately managing and locating goods in warehouses has become key to enhancing operational efficiency. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology, as an advanced automatic identification and data collection technology, is increasingly being applied in warehouse management. This article will discuss the role of RFID readers and tags in warehouse goods localization, and illustrate the advantages and disadvantages of different frequency RFID systems through specific project examples.
Overview of RFID Technology
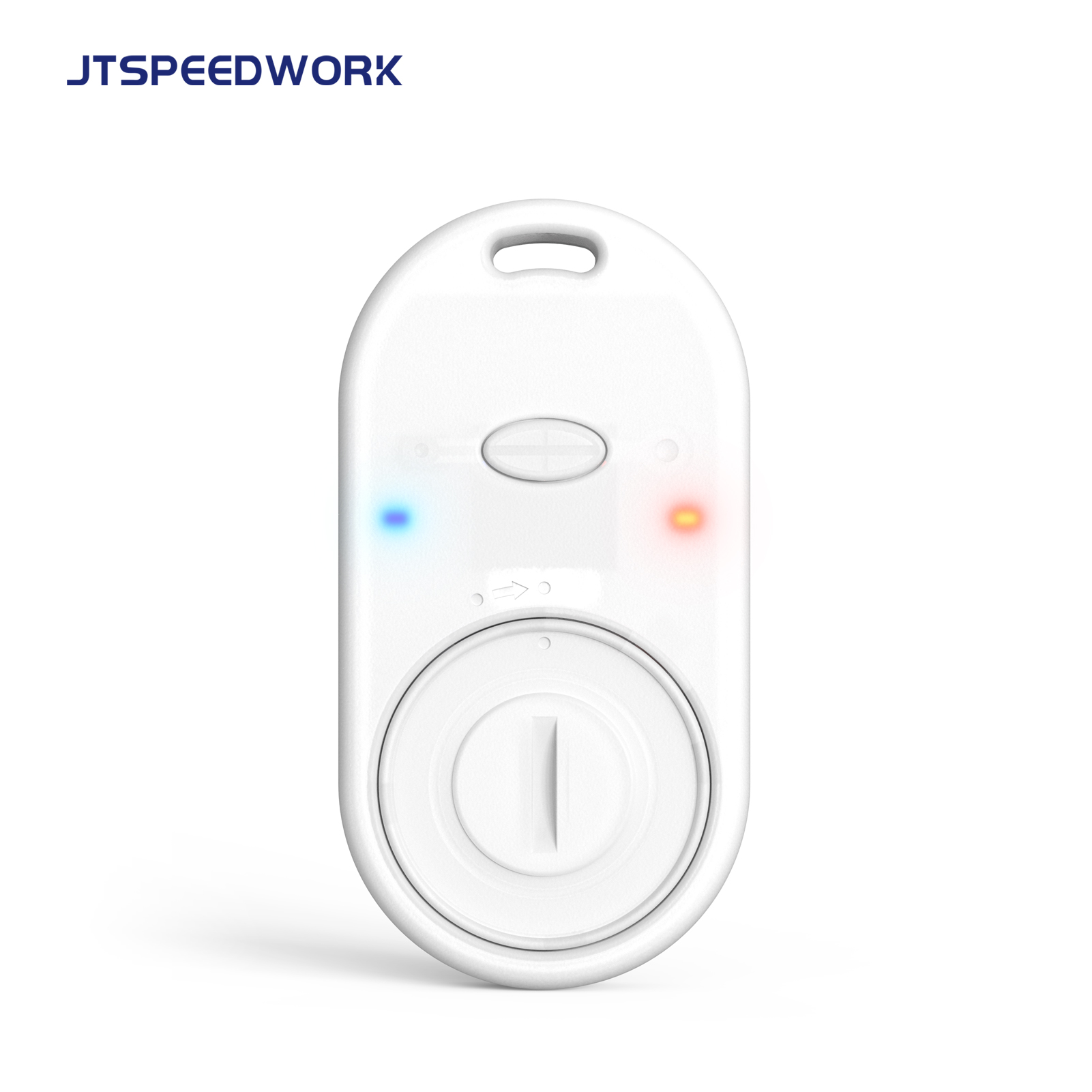
RFID technology transmits data through radio waves and mainly consists of RFID tags and RFID readers. Tags are attached to items and contain a small antenna and a chip to store information about the items, while readers are used to read and write data from and to the tags. Based on different operating frequencies, RFID systems can be divided into three categories: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra High Frequency (UHF).
Low Frequency (LF) RFID Systems
Advantages
- Strong Penetration Ability: LF RFID systems operate in the frequency range of 30 kHz to 300 kHz, and their signals can penetrate water and non-metallic materials, making them suitable for humid and obstacle-rich environments.
- Lower Cost: The production cost of LF RFID tags and readers is relatively low, suitable for cost-sensitive applications.
Disadvantages
- Short Reading Distance: LF RFID typically has a reading distance of only a few centimeters to tens of centimeters, limiting its application in wide-range goods localization.
- Low Data Transmission Rate: LF RFID has a low data transmission rate, unsuitable for scenarios requiring rapid reading of a large number of tags.
Application Example
In a food processing company's warehouse, due to the high humidity and the need to penetrate packaging materials to read information, an LF RFID system is used to track and manage goods. In this case, the LF RFID system can ensure stable performance in humid environments. However, due to its short reading distance, the company had to install more readers to cover the entire warehouse, increasing the system's complexity.
High Frequency (HF) RFID Systems
Advantages
- Moderate Reading Distance: HF RFID systems operate in the frequency range of 3 MHz to 30 MHz, with a reading distance generally between a few centimeters and one meter, suitable for medium-range item tracking.
- Strong Anti-interference Ability: HF RFID performs well in environments with metallic objects and has strong anti-interference capabilities.
Disadvantages
- Moderate Cost: Compared to LF systems, HF RFID is slightly more expensive but still within an acceptable range.
- Moderate Reading Speed: The reading speed of HF RFID is faster than LF RFID but not as fast as UHF RFID, suitable for medium-speed reading requirements.
Application Example
In a clothing retail company's warehouse, HF RFID systems are used to manage and locate goods. Clothing is usually made of different materials, and HF RFID tags can effectively read the information of tags wrapped in various materials, providing accurate goods localization. Despite its limited reading distance, it still operates effectively in a rela
tively concentrated warehouse environment.
Ultra High Frequency (UHF) RFID Systems
Advantages
- Long Reading Distance: UHF RFID systems operate in the frequency range of 300 MHz to 3 GHz, with reading distances reaching several meters to even tens of meters, ideal for wide-range goods tracking.
- Fast Reading Speed: UHF RFID has a high data transmission rate, capable of quickly reading large numbers of tags, enhancing warehouse operational efficiency.
- Large Tag Capacity: UHF RFID tags can store more information, facilitating complex inventory management.
Disadvantages
- Higher Cost: UHF RFID systems have higher tag and reader costs, suitable for companies with sufficient budgets.
- Susceptibility to Interference: UHF RFID systems are more prone to interference in environments with metal and water, which may affect reading performance.
Application Example
In a large e-commerce warehouse, a UHF RFID system is used to manage and locate a vast number of goods. The warehouse handles various types of goods in large quantities, and UHF RFID's long reading distance and fast reading capability can effectively handle the high frequency and large volume of goods entering and leaving the warehouse. Additionally, deploying a few high-performance readers can cover a large warehouse area, reducing system complexity and deployment costs.